AI chatbots use generative AI to provide responses based on a single interaction. A person makes a query and the chatbot uses natural language processing to reply.
The next frontier of artificial intelligence is agentic AI, which uses sophisticated reasoning and iterative planning to autonomously solve complex, multi-step problems. And it’s set to enhance productivity and operations across industries.
Agentic AI refers to AI systems and models that can act autonomously to achieve goals without the need for constant human guidance. The agentic AI system understands what the goal or vision of the user is and the context to the problem they are trying to solve.
These models differs from generative AI models in several ways:
- They are focused on making decisions rather than on creating content.
- They do not rely on human prompts, but rather are set to optimize particular goals or objectives, such as maximizing sales, customer satisfaction scores, or efficiency in supply-chain processes.
- Unlike generative AI, agentic AI can carry out complex sequences of activities, independently searching databases or triggering workflows to complete activities.
Agentic AI systems promise to transform many aspects of human-machine collaboration, especially in areas of work that were previously insulated from AI-led automation, such as proactively managing complex IT systems to pre-empt outages; dynamically re-configuring supply chains in response to geopolitical or weather disruptions; or engaging in realistic interactions with patients or customers to resolve issues.
Greater workspace specialization, greater informational trustworthiness, and enhanced innovation will be main benefits.
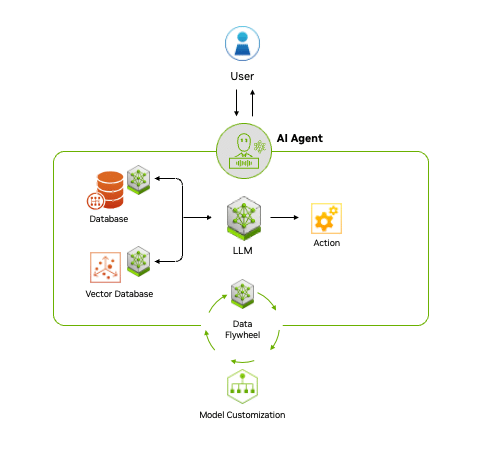
Agentic AI uses a four-step process for problem-solving:
- Perceive: AI agents gather and process data from various sources, such as sensors, databases and digital interfaces. This involves extracting meaningful features, recognizing objects or identifying relevant entities in the environment.
- Reason: A large language model (LLM) acts as the orchestrator, or reasoning engine, that understands tasks, generates solutions and coordinates specialized models for specific functions like content creation, vision processing or recommendation systems. This step uses techniques like retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to access proprietary data sources and deliver accurate, relevant outputs.
- Act: By integrating with external tools and software via application programming interfaces, agentic AI can quickly execute tasks based on the plans it has formulated. Guardrails can be built into AI agents to help ensure they execute tasks correctly. For example, a customer service AI agent may be able to process claims up to a certain amount, while claims above the amount would have to be approved by a human.
- Learn: Agentic AI continuously improves through a feedback loop, or “data flywheel,” where the data generated from its interactions is fed into the system to enhance models. This ability to adapt and become more effective over time offers businesses a powerful tool for driving better decision-making and operational efficiency.
The potential applications of agentic AI are vast, limited only by creativity and expertise. From simple tasks like generating and distributing content to more complex use cases such as orchestrating enterprise software, AI agents are transforming industries.

Despite significant potential to transform human-machine collaboration and drive greater efficiency and business growth, agentic AI systems are still at a relatively early stage of development.